Rudolph Virchow, German Polymath

by Science Source
Title
Rudolph Virchow, German Polymath
Artist
Science Source
Medium
Photograph - Photograph
Description
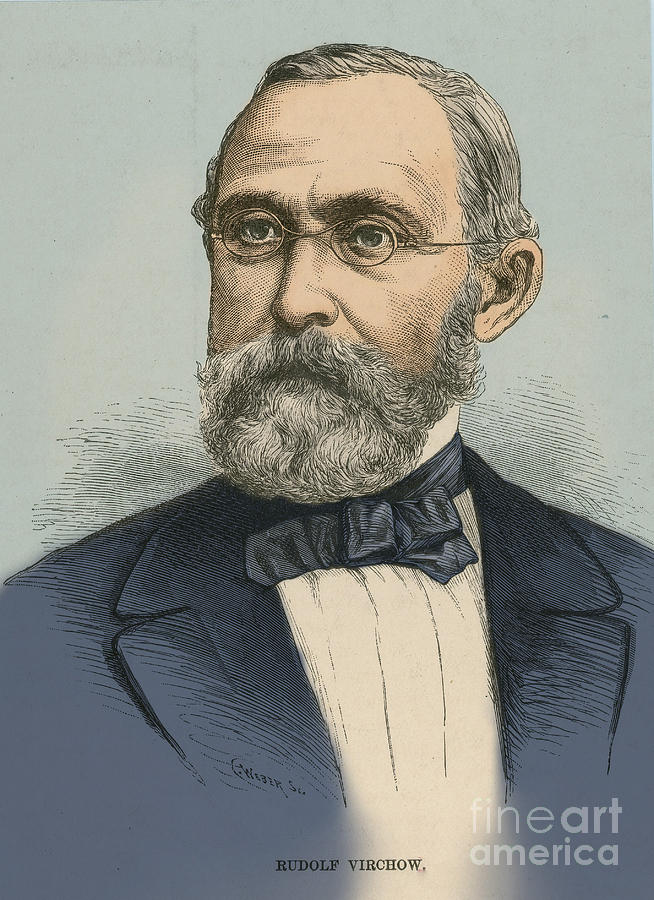
Rudolph Carl Virchow (1821-1902) was a German doctor, anthropologist, pathologist, prehistorian, biologist and politician, known for his advancement of public health. Referred to as "the father of modern pathology," he is considered one of the founders of social medicine. Virchow is credited with multiple important discoveries. Virchow's most widely known scientific contribution is his cell theory, which built on the work of Theodor Schwann. He is cited as the first to recognize leukemia cells. Another significant credit relates to the discovery, made approximately simultaneously by Virchow and Charles Emile Troisier, that an enlarged left supra-clavicular node is one of the earliest signs of gastrointestinal malignancy and has become known both as Virchow's node and Troisier's sign. Virchow described the factors contributing to venous thrombosis, Virchow's triad and coined the term embolism. He founded the medical fields of cellular pathology and comparative pathology. In response to a lack of standardization of autopsy procedures, he established and published specific autopsy protocols. Virchow was an advocate for social and political reform stating, "The physicians are the natural attorneys of the poor, and social problems fall to a large extent within their jurisdiction." He died of heart failure in 1902 at the age of 80.
Uploaded
March 7th, 2013
Embed
Share
Comments
There are no comments for Rudolph Virchow, German Polymath. Click here to post the first comment.